Selected Publications
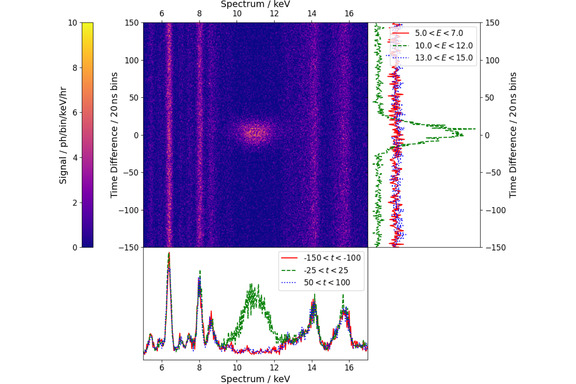
We present measurements of X-ray Parametric Down Conversion at the Advanced Photon Source synchrotron facility. Using an incoming pump beam at 22 keV, we observe the simultaneous, elastic emission of down-converted photon pairs generated in a diamond crystal. The pairs are detected using high count rate silicon drift detectors with low noise. Production by down-conversion is confirmed by measuring time–energy correlations in the detector signal, where photon pairs within an energy window ranging from 10 to 12 keV are only observed at short time differences. By systematically varying the crystal misalignment and detector positions, we obtain results that are consistent with the constant total of the down-converted signal. Our maximum rate of observed pairs was 130/h, corresponding to a conversion efficiency for the down-conversion process of 5.3±0.5×10−13.
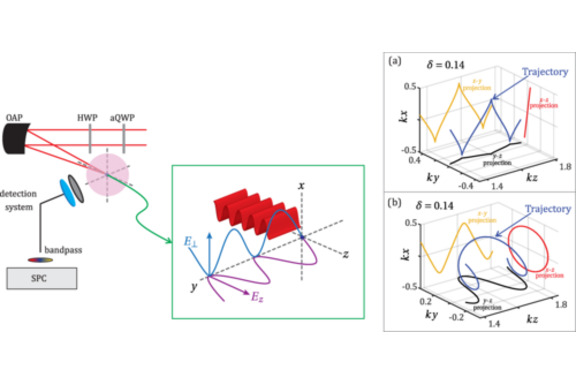
We report experimental results from a study of nonlinear Thomson scattering of elliptically polarized light. Polarization-resolved radiation patterns of the scattered light are measured as a function of the elliptical polarization state of the incident laser light. The relativistic electron trajectory in intense elliptically polarized fields leads to the formation of unique radiated polarization states, which are observed by our measurements and predicted by a theoretical model. The polarization of Thomson scattered light depends strongly on the intensity of the incident light due to nonlinearity. The results are relevant to high-field electrodynamics and to research and development of light sources with novel capabilities.
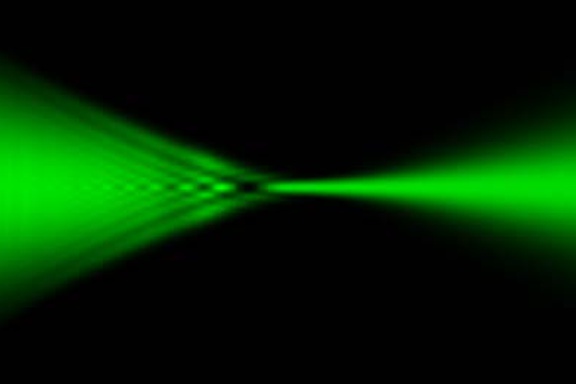
Photophoresis can trap opaque microscopic particles in a focused laser beam surrounded by a gas such as air. The particle is heated by the laser, and in turn, interactions with the ambient gas provide a stabilizing force that holds the particle in a specific region of the beam. The particles can stay trapped while the beam is moved side to side up to 2 m/s, enabling three-dimensional images to be traced out in a display application. Structure in the laser beam is associated with the trapping phenomenon, but the fundamental mechanism for stability of the trap remains mysterious. Particles prefer regions of the beam with diffraction features such as those that arise from spherical aberration. Nevertheless, the ability of near-unidirectional light, albeit light that undergoes focusing and exhibits structure, to provide a restor-ing force to trapped particles in the direction opposite to beam propagation needs to be explained. Through repeated trials of capturing particles in a well characterized beam, we map out the preferred locations for particle capture and correlate them with diffraction features of the beam. The specific beam locations that host trapped particles, when compared with neighboring regions that do not, can offer insight into the stability mechanism. We analyze the Poynt-ing vector in the vicinity of trapped particles. The flow of light energy can provide important clues into the trapping mechanism.