Selected Publications
S. Glasgow, M. Ware, and J. Peatross
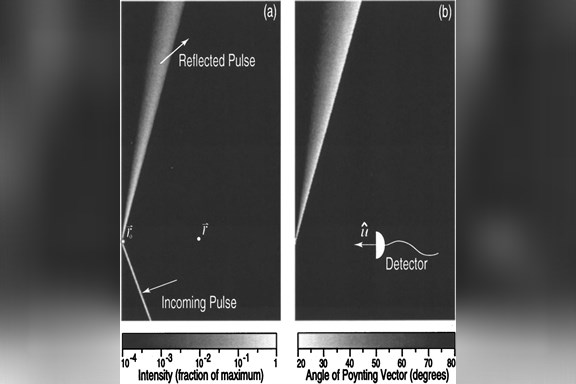
Without approximation the energy density in Poynting's theorem for the generally dispersive and passive dielectric medium is demonstrated to be a system total dynamical energy density. Thus the density in Poynting's theorem is a conserved form that by virtue of its positive definiteness prescribes important qualitative and quantitative features of the medium-field dynamics by rendering the system dynamically closed. This fully three-dimensional result, applicable to anisotropic and inhomogeneous media, is model independent, relying solely on the complex-analytic consequences of causality and passivity. As direct applications of this result, we show (1) that a causal medium responds to a virtual, "instantaneous" field spectrum, (2) that a causal, passive medium supports only a luminal front velocity, (3) that the spatial "center-of-mass" motion of the total dynamical energy is also always luminal and (4) that contrary to (3) the spatial center-of-mass speed of subsets of the total dynamical energy can be arbitrarily large. Thus we show that in passive media superluminal estimations of energy transport velocity for spatially extended pulses is inextricably associated with incomplete energy accounting.
Justin Peatross, Michael Ware, and Scott A. Glasgow
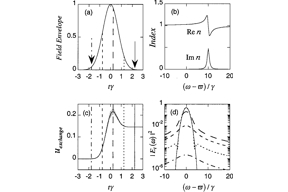
A model-independent theorem demonstrates how a causal linear dielectric medium responds to the instantaneous spectrum, that is, the spectrum of the electric field pulse that is truncated at each new instant (as a given locale in the medium experiences the pulse). This process leads the medium to exchange energy with the front of a pulse differently than with the back as the instantaneous spectrum laps onto or off of nearby resonances. So-called superluminal pulse propagation in either absorbing or amplifying media as well as highly subluminal pulse propagation are understood qualitatively and quantitatively within this context. (C) 2001 Optical Society of America.
Light-pulse propagation in angularly dispersive systems is explored in the context of a center-of-mass definition of energy arrival time. In this context the time of travel is given by a superposition of group delays weighted by the spectral content of the pulse. with this description the time of travel from one point to the next for a pulse is found to be completely determined by the spectral content, independent of the state of chirp. The effect of sensor orientation on arrival time is also considered. (C) 2001 Optical Society of America.